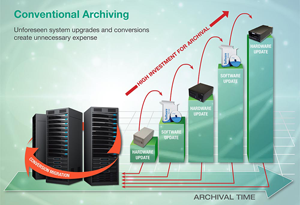
Conventional archiving methods are associated with significant drawbacks, which are familiar in any company.
- They require intensive use of personnel.
In both the planning and the execution, a company must regularly commit a substantial amount of staff time to archiving. Furthermore, often the processes can only be carried out by certain employees, who are then unable to carry out other duties during the archiving periods. - They consume immense amounts of money.
Apart from the high payroll costs, providing the necessary archiving hardware is expensive. Regular investment must also be made in updates and procuring the next generation of backup software and storage media. - They are a source of risk when the archive data is migrated back to the company IT systems.
It is often not discovered until the data is re-migrated from the archive that, although it is readable it is almost impossible to integrate. The software has undergone updates, version jumps or generation changes, and as a result it is very difficult to use the archive data in the current environment. - The often do not satisfy compliance requirements.
Archiving arrangements are subject to various legal requirements, including GDPdU, GoBS, Basel II and so on. Most companies also implement their own in-house regulations governing the long-term storage of business-related electronic documents. The way corporate data should be stored to ensure compliance with these regulations is a frequently debated topic, and in many cases it is of direct significance with regard to obtaining certifications, which many companies actively pursue.
Conventional archiving methods have serious disadvantages!